Your diet plays a big role in body functions. There’s usually a big fuss, especially on dietary fats and oils you use to cook and dress your salads. Many heart experts also emphasize avoiding trans fats and moderating saturated fats consumption because they are cardiovascular risk factors.
When talking coconut oil, there are many products from it besides the edible oil. One common one is coconut oil for your hair. You can use it to moisturize and prevent hair breakage.
What will we be looking at in this article today you ask? You will learn more about the the protein in coconut oil, and its function role in hair treatment. Let’s get to it!
Is Coconut Oil Protein or Moisture for Hair?
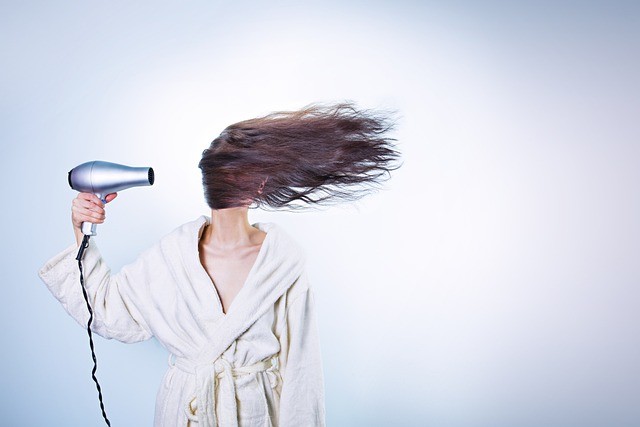

According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), a tablespoon of coconut fat contains (11.6g) contains 0 g of protein.
Coconut Oil and Protein
Coconut oil is not a protein but it does behave like a protein because of its ability to penetrate the hair shaft but does not do the build-work reserved for proteins. If you are protein-sensitive, this option may be a great treatment option for your hair.
However, coconut oil is made up mostly of fats. It is made up of 50% MCTs of saturated fat and 5% unsaturated fats. The type of saturated fat found in coconut oil is medium-chain triglycerides which can have numerous health benefits for your hair.
The medium-chain fatty acids are caprylic acid, caproic acid, capric acid, and lauric acid. Although lauric acid is considered medium-chain triglyceride, it behaves like long-chain fatty acids. Your coconut hair product is less expensive and less processed than MCT oils and can be a better choice for hair treatments.
Coconut Oil and Moisture
It is more of a moisturizer for hair than a source of protein due to its high saturated fat content. The fatty acids lock in water in the hair reducing water loss and promoting hydration of your hair shafts.
Is Coconut Oil Good for Protein Overload?

Stop thinking of eating itl and shift your focus to the other benefits of coconut oil. Yes, your hair is one of them! Okay, now you’re talking!
What is Protein Overload?
Protein overload refers to the moisture and protein imbalance due to excess protein in your hair.
I know it sounds crazy that there’s too much protein in your hair considering it is made up of mostly protein. Too much protein depends on an individual’s hair, it’s not a one size fits all kind of situation. It may be very difficult to realize protein overload because its symptoms are similar to those of other hair conditions like dry hair.
Symptoms of Protein Overload
- Shedding
- Lack of hair shine
- Dry and brittle hair
- Stiff hair
- Tangling in hair
Protein in Coconut Oil for Protein Overload
In cases where you suffer from protein overload, you want to avoid hair products with protein for your hair treatment. Although the levels of protein in coconut oil are low, it prevents protein loss from your hair and increases moisture levels.
In a study comparing the health effects of sunflower oil, coconut oil, and mineral oil on hair damage, evidence showed that only coconut oil reduced protein loss in both damaged and undamaged hair. Coconut oil had a greater impact on hair healing and growth compared to both sunflower oil and mineral oil.
If you’re looking to fix a dry scalp issue or increase volume, then coconut oil is for you. However, in terms of protein overload, it will prevent the loss of protein making the issue worse. For protein overload, protein in coconut oil is a no-no!
Is Coconut Oil Good for Low Porosity Hair?
What does it mean to have low-porosity hair? Low porosity hair is the type of hair with fewer tiny openings and small-sized pores within each hair strand. The struggle with this type of hair is it is more difficult to style and keep moisturized since the cuticles lie flat against the shaft and are tightly packed making them more resistant to moisture.
Symptoms of Low Porosity Hair
Here are the telltales to look out for to know if your hair is the low porosity kind:
- There’s always a buildup of product on the surface of your scalp.
- You at times observe water beads on the surface of your hair.
- Your hair takes longer to dry up or to get wet.
- Your hair texture is rough and coarse.
- Product absorption is slow.
- Protein treatment doesn’t work. Applying protein-rich products stiffens your hair.
- You use too many products to achieve the results you desire.
Coconut oil may not be the best option for low-porosity hair. You will observe either one of the following when you use it on your low-porosity hair:
- Your hair feels straw-like and brittle
- It sits on the surface of your hair rather than penetrating the hair shaft
Coconut oil is not good for low-porosity hair since it solidifies easily and leads to product buildup in your hair. Because the cuticles are already tightly packed and flat against your hair shaft your hair will struggle to absorb this product fast enough. Your hair feels like straw because of the low viscosity of the coconut liquid.
What happens to your hair when a cold winter breeze passes through it? It stiffens, right? Coconut oil solidifies at a fairly low temperature which is why it stiffens low-porosity hair.
How to Use Coconut Oil for Low Porosity Hair
The fact that it is not good for low-porosity hair doesn’t mean you should scrap it off from your hair regimen. Use these tips to benefit from coconut hair liquid to promote hair health.
Use only a little of it to go a long way. After application, wear a shower cap for half an hour or pass hot air from your blow dryer to help relax your cuticles to allow the coconut oil to penetrate your scalp.
How to Use Coconut Oil for High Porosity Hair

Coconut oil may not be the best bet for low-porosity hair, but the reverse is the case for high-porosity hair. This hair type absorbs and loses moisture easily because its cuticle layer is open and loosely packed.
Coconut will help lock in moisture into your high-porosity hair keeping it hydrated for longer. For people with dry, rough, and rigid hair, this tropical oil will bind to the proteins of your hair naturally reinforcing your hair fiber and maintaining its natural moisture.
Here are some tips to use coconut for high-porosity hair:
Heat then Use
The best way is to use it as a hot oil treatment. Coconut oil solidifies fast and can cause product buildup in your hair. Heat some coconut oil in a saucepan until hot. Check the temperature of your oil before applying it to your hair.
Use a comb to section your hair and apply the hot coconut treatment. Cover with a shower cap overnight.
Coconut Conditioner

After shampooing your hair, warm some coconut oil in your hands and comb it through sections of your hair slowly. Avoid the roots of your hair if you have hair that absorbs oil too quickly. Focus on the hair shafts and split ends. Don’t wash out the oil.
How About A Hair Mask?
You can mask your hair with coconut oil. Saturate sections of your hair with this oil working your way from root to ends. Cover with a shower cap at any time from half an hour to overnight. Once satisfied, wash out with a conditioner.
Other tips include using unrefined, virgin coconut oil, melting your oil before use, and making a cocktail of hair treatments. Consider using coconut oil with other oils like extra virgin oil and essential oils and ingredients that promote hair health. An onion juice and coconut oil hair mask for hair loss isn’t the craziest idea!
The best way for your hair to benefit is through coconut oil consumption. Incorporate it in place of vegetable oils and soybean oil into your diet to get the fatty acids your hair needs for growth.
Other plant-based oils and other fats may not be the best choices for cooking because of their smoke points. The urefined variety has a lower smoke point while the refined kind has a higher smoke point. Extra virgin coconut oil is a better choice for low-temperature cooking while refined option is better for high-temperature cooking methods.
Besides, one tablespoon of coconut gives you similar benefits plus a sweet flavor without the product build-up mess that comes with applying it to your hair. Edible oil is the better choice!
Coconut Oil Benefits and Side Effects
Let’s start with the pros of using it:
Antioxidant properties
Virgin coconut oil contains polyphenolic antioxidants that increased its scavenging properties for reactive oxygen species. It contains ferulic acid and p-coumaric acid which reduce inflammation preventing chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Weight Loss
An open pilot study to assess the efficacy of virgin coconut oil in reducing visceral adiposity showed that coconut oil was efficient in weight loss among men. There was no change in blood lipids, but a reduction in creatinine and alanine transferase levels was observed.
There was a reduction in belly fat observed through the reduction of waist circumference. Coconut consumption is less likely to trigger weight gain and obesity compared to other oils like soybean oil.
Some research reports that although coconut oil consumption increased HDL cholesterol levels and reduced LDL cholesterol, it did not affect weight and body fat. More research should be done to investigate how it manages weight.
Improve Cognitive Function and Brain Health
There’s no pharmacologic drug that can prevent or treat Alzheimer’s disease. A study carried out on patients with Alzheimer’s dementia consuming 40ml/day of virgin oil reported an increase in cognitive status.
How does coconut oil improve brain health and cognitive function? Mild cognitive impairment is brought about by the deregulation of brain glucose metabolism. Coconut’s MCTs are broken down to produce ketone bodies which are the brain’s preferred source of energy.
The dietary roles of coconut oil in the suppression of neuro-inflammation, including reversing neurodegeneration are attributed to the benefits of ketones on brain health.
Nutrient-Rich Food
One tablespoon of coconut contains 0.013mg of vitamin E and 0.116g of calcium. It is also a good source of manganese which plays a significant role in the metabolism of cholesterol, carbohydrates, and proteins. It also contains copper and iron which are used in red blood cell production and selenium which is an antioxidant.
Increases Absorption of Vitamin D
Coconut oil increases the absorption of fat-soluble vitamin D. The MCTs also help absorb more of this vitamin compared to other fats with short-chain fatty acids. The elderly who are at a higher risk of osteoarthritis are usually advised to consider MCT supplementation to improve vitamin D absorption which contributes to the maintenance of normal muscle function and bone building and strengthening.
Skin Health Benefits
The saturated fats in coconut oil (lauric acid and capric acid) have antimicrobial health benefits against bacteria causing skin infections like acne and cellulitis. A comparative study showed that lauric acid had greater anti-bacterial properties against P.acnes than capric acid, both saturated fats in coconut oil. This means that coconut oil is good for your skin’s health.
It is also perfect for skin health of dry skin since it locks in moisture and reinforces the skin’s natural barrier. A random study comparing the effectiveness of coconut oil to mineral oil as a moisturizer for mild to moderate xerosis showed more improvement in skin hydration and an increase in skin surface lipid levels when using coconut oil than mineral oil.
Other health benefits to the skin include acne treatment, healing, reduced inflammation, and anti-aging benefits.
Side Effects of Coconut Oil
There are negative effects to excess consumption of coconut oil. Too much consumption of refined coconut oil or processed coconut oil can lead to elevated cholesterol levels compared to nontropical vegetable oils since it is high in saturated fats. High LDL cholesterol levels increase cardiovascular risk factors.
Although other saturated fats are healthy, it is important to consume foods rich in these saturated fatty acids in moderation. If you’re looking for oils to consume in high amounts opt for extra virgin olive oil that is rich in unsaturated fats lowering your risks of cardiovascular disease.
Besides the effects of saturated fats on cardiovascular risk factors, extra virgin coconut oil can cause allergies. You can have hives to anaphylaxis reactions to this oil. Speak to your healthcare provider if you show any signs of reacting to coconut oil. Some of the symptoms include skin irritation, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal distension, and vomiting.
Is Coconut Better than Olive Oil?
For healthy eating, choose olive oil over coconut oil. Olive oil is richer in polyunsaturated fats and medium-chain triglycerides and contains lower amounts of saturated fat. Extra virgin oil lower your risks of heart problems and other chronic conditions.
However, when cooking with heat above 300°F (149°C), it is healthier to use coconut oil than olive oil. This is because coconut oil has a high smoke point compared to olive oil.
The smoke point of coconut oil is 350°F and that of olive oil is 280°F. Use coconut oil for frying, sautéing, and baking and olive oil for pan-frying, and medium-heat cooking. Extra virgin olive oil is the best choice for dressings since it has a strong flavor.
Which Oil is Best for Protein Overload Hair?
Extra virgin coconut oil is off the table for protein overload, but what can you use to reduce protein buildup in your hair?
Essential oils are the best options for protein overload treatment. Go for Sage, Lavender, and Peppermint when trying to reduce protein in your hair treatment.
You will add your essential oil to a carrier hair treatment like onion juice then apply it on your scalp to promote blood flow and hair growth.
Bottom Line
There are small amounts of protein in coconut oil. In addition, the American Heart Association advises replacing coconut oil with other MUFA and PUFA-rich oils. This doesn’t mean you should do away with coconut oil completely from your diet. Use it in moderation and you will enjoy its benefits while eating keto. There are so many keto recipes you can incorporate coconut oil into to reap its benefits.
What’s your hair type when classifying in terms of porosity? Have you used coconut oil as part of your hair treatment? What do you observe when you use coconut oil in your hair?
Are there other ways you have incorporated coconut oil into your lifestyle? Which benefits have you reaped since you started using this tropical oil? Would you recommend this oil to other dieters? Leave your answers in the comment section below!